Publications
Publications from the SIMI Lab reflect our mission to advance AI-enabled surgical intelligence through close integration of computer vision, machine learning, and clinical neurosurgery. Our work focuses on developing and validating computational tools that support intraoperative guidance, decision-making, and improved surgical outcomes in real-world operating rooms.
Major Publications
2026
Arachnoid Membrane Segmentation in Intraoperative Microscopic MVD Surgery Scenes
MICCAI Workshop 2025 (COLAS)
Abstract: Microvascular decompression (MVD) is a neurosurgical procedure to treat cranial nerve compression syndromes such as trigeminal neuralgia and hemifacial spasm. The arachnoid membrane (AM) is a thin, transparent meningeal layer that adheres to or covers neurovascular structures and must be carefully dissected to access the surgical site during MVD surgery. Proper AM dissection is essential for visualizing the operative field and ensuring safe vessel and nerve manipulation. However, AM dissection is technically challenging due to its poor contrast with surrounding tissues and close adherence to critical neurovascular structures. To address this, we propose the first dedicated study on AM segmentation from operative MVD videos. We introduce a highquality, expert-annotated dataset focusing on AM in the cerebellopontine angle and train a segmentation model with a task-specific loss function to improve AM segmentation. Our results demonstrate that the proposed loss function improves AM segmentation performance by 7.35% in IoU over the baseline, enabling reliable segmentation despite the membraneâĂŹs transparency and intraoperative variability. This work lays the foundation for automated AM recognition in surgical environments and provides a valuable resource for AM dissection and surgical decisionmaking.
2025
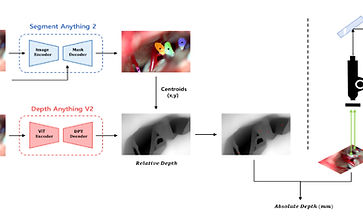
Intraoperative Absolute Depth Estimation in MVD Surgery
CBMS 2025
Abstract: Microvascular decompression (MVD) is a neurosurgical procedure that relieves nerve compression by repositioning or separating offending blood vessels, effectively reducing pain or spasms. Accurate localization of the compression site is crucial for optimal surgical outcomes, as it enables precise identification and decompression of the offending vessel. While horizontal anatomical relationships are easily identified in the surgical view, compressions occurring along the depth axis are more challenging to discern. In this study, we propose a method to measure accurate intraoperative distances during MVD surgery using DepthAnything-V2. By leveraging the optical properties of standard imaging equipment in conjunction with the depth estimation model, our method computes precise, absolute distances rather than relying solely on relative measurements, achieving distance estimation errors of less than 2 mm compared to intraoperative and preoperative reference measurements.
2023
Developing the surgeon-machine interface: using a novel instance-segmentation framework for intraoperative landmark labelling